Complex diagnostics system for equipment of a reactor facility’s primary circuit

Functions of KSD:
- deep complex technical diagnostics of main equipment of an RF’s primary circuit using comparison and analysis of diagnostic information received from power unit’s instrumentation and control systems, local diagnostics systems, and own databases;
- providing a diagnostic engineer with centralized access to operating and archive diagnostic information received from different sources (IVS, ASRK, etc.) and allowing to determine and forecast technical state of operated RF’s primary circuit equipment;
- transferring parameters to be displayed to personnel to a unit’s local area network.
Composition of KSD:
- KSD’s upper level system;
- vibration and noise diagnostics system SVRShD;
- loose parts monitoring system SOSP;
- system of RF’s primary circuit coolant leakage monitoring SKPT;
- system for vibration monitoring and diagnostics of reactor coolant pumps SVKD GCN;
- fatigue monitoring system SDOR;
- system of pipeline displacement monitoring SKPTr.
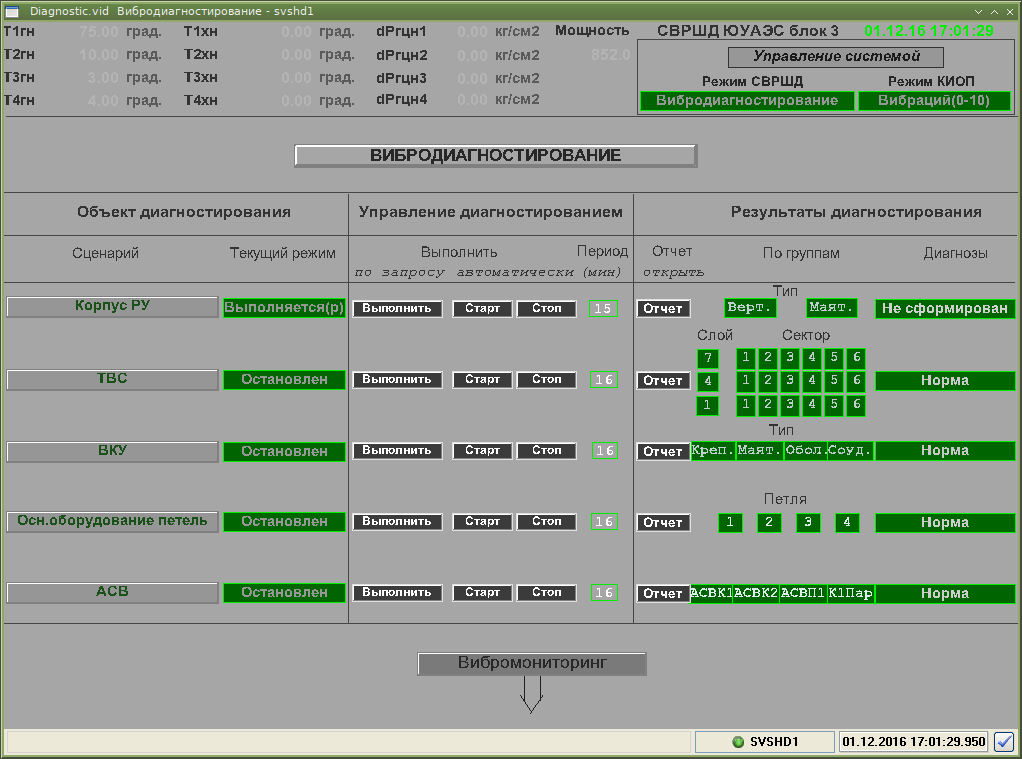
Vibration and noise diagnostics system SVRShD
The system is intended for monitoring and diagnostics of vibration state of primary circuit equipment, to monitor:
- trajectory of thermal displacement of primary circuit main equipment in heating/cooling modes for detection of non-project displacement trajectories caused by defects in pillars of monitored equipment;
- vibration state of primary circuit main equipment, including a reactor vessel, for detection of abnormal vibrations caused by change in pillar rigidity, weakening of equipment attachment points, or intensification of vibration causing forces;
- vibration state of fuel rod assemblies for detection of abnormal vibrations caused by weakening of attachment points or intensification of coolant influence;
- vibration state of a reactor shaft for detection of abnormal vibrations caused by wearout of attachment points or intensification of coolant influence.
Functions of SVRShD:
- inputting, converting, and comparing with setpoints signals from vibration sensors, vibration displacement sensors, neutron detection units, and direct charge sensors;
- receiving information on RF technological parameters from power unit’s IVS;
- archiving monitoring and diagnostic data;
- calculated diagnostics of vibration state considering current and archive data, generating reports;
- transferring information on state of diagnosed equipment to a computing server of KSD.
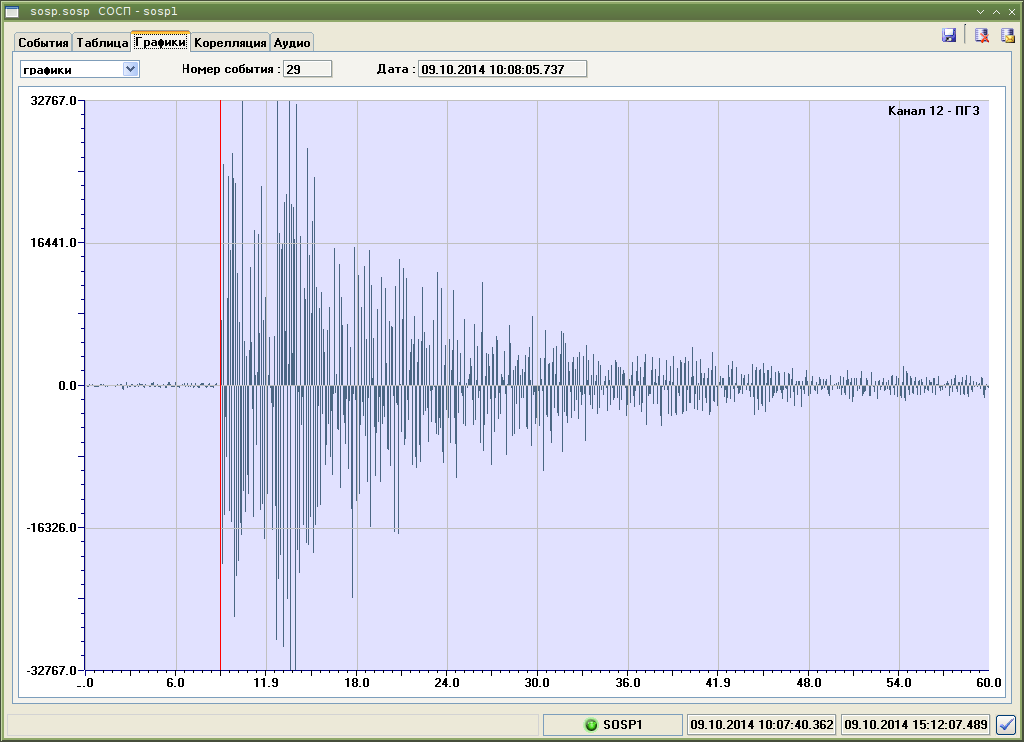
Loose parts monitoring system SOSP
The system is intended for early detection and determination of location of loose parts and poorly fixed equipment details in coolant stream using acoustic sensors installed on the surface of RF’s primary circuit equipment.
Functions of SOSP:
- inputting, converting, and comparing with setpoints noise signals from acoustic sensors;
- monitoring vessel noise of main equipment and primary circuit pipelines, detecting loose and poorly fixed parts in coolant stream;
- archiving data, listening and recording acoustic signals;
- monitoring operability of channels that receive and process signals of sensors;
- displaying diagnostics results to an operator and transferring to a computing server of KSD.
System of primary circuit coolant leakage monitoring SKPT
The system is intended to monitor tightness of equipment and pipelines of main circulation circuit, to detect RF’s primary circuit coolant leakage in time, to assess its magnitude in normal operation modes, with deviations from normal operation, and in a “small leakage” mode.
Functions of SKPT:
- inputting, converting, and comparing with setpoints signals from humidity and temperature sensors, acoustic sensors;
- receiving information from a power unit’s process information system;
- complex analysis on localization and determining magnitude of leakage;
- transferring diagnostics results to a computing server of KSD and displaying to an operator;
- generating warning alarm.
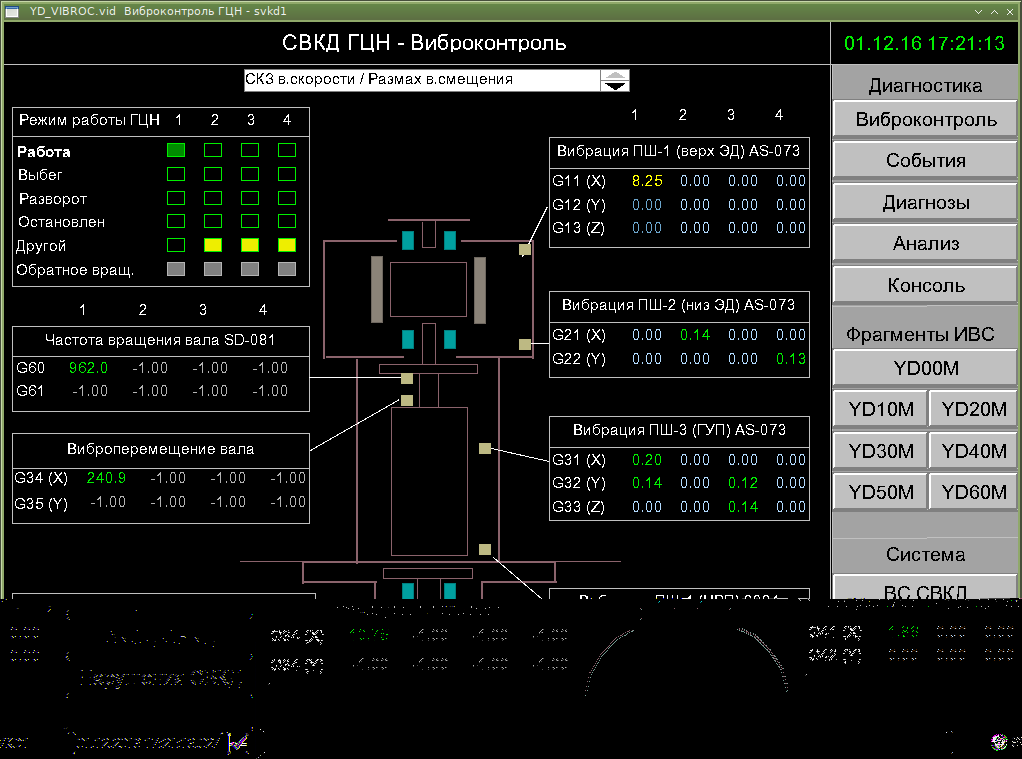
System for vibration monitoring and diagnostics of reactor coolant pumps SVKD GCN
The system is intended for monitoring of vibrational parameters of reactor coolant pumps (GCN) for early detection of abnormal states of mechanical and electrical parts, technical state forecasting based on complex analysis of vibrational characteristics and thermal parameters.
Functions of SVKD GCN:
- continuously monitoring GCN vibrational state and identifying slowly developed defects;
- monitoring vibrational characteristics in different modes of GCN operation, including rotor rundown mode during electric motor power supply shutdown;
- analyzing, archiving, and logging data;
- diagnosing GCN state with display of results to a diagnostic engineer and generation of alarm.
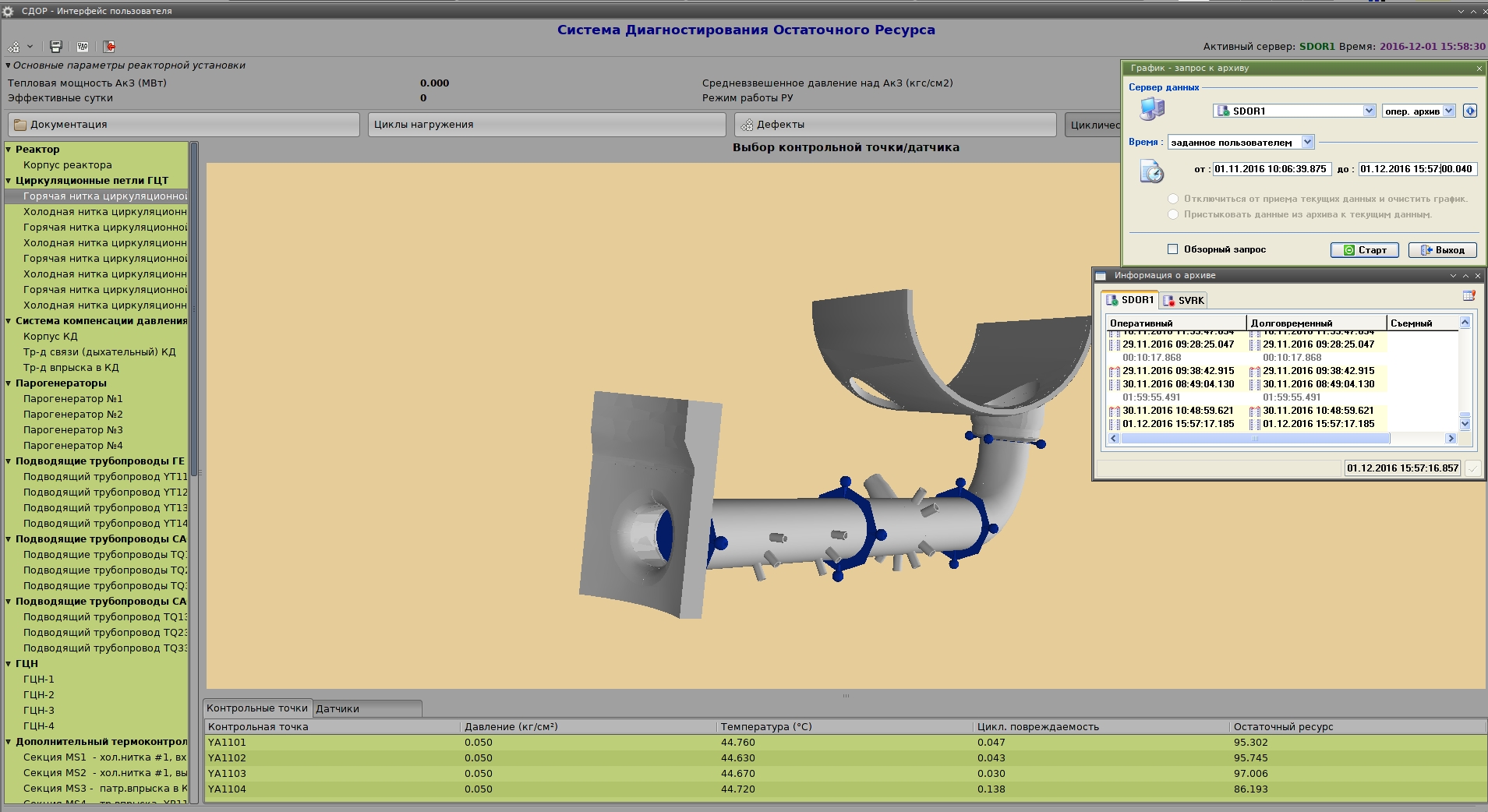
Fatigue monitoring system SDOR
The system is intended to calculate cumulative fatigue damage dealt to metal in the most stressed points of a structure and to evaluate remaining lifetime of elements of main equipment of the RF’s primary circuit based on continuous monitoring of thermotechnical parameters in different modes of operation.
Functions of SDOR:
- inputting and converting signals from thermal control sensors (monitoring of thermal pulsations and coolant stratification), collecting and accumulating information received from a computing server of KSD;
- calculating fatigue damage and remaining lifetime in control (the most stressed) points;
- assessing remaining lifetime of equipment and pipeline metal;
- maintaining databases, registering signals received from IVS, KSD, and own sensors.
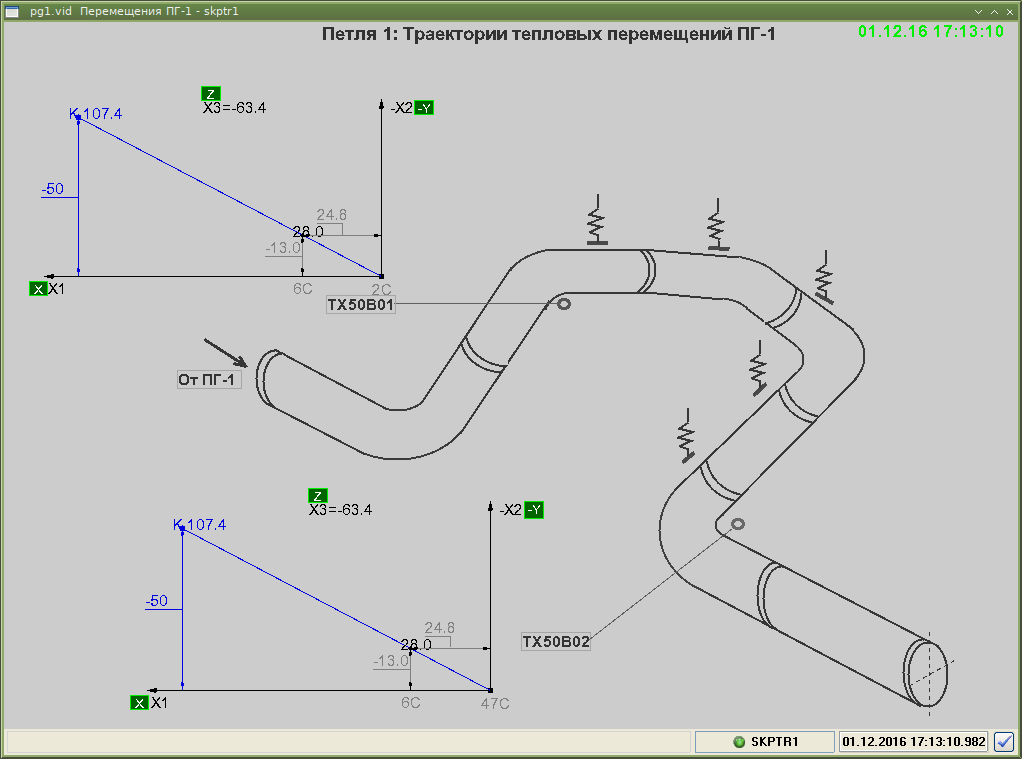
System of pipeline displacement monitoring SKPTr
The system is intended to measure continuously and to record maximum pipeline displacements under conditions of power unit normal operation and transient modes.
Functions of SKPTr:
- receiving and processing signals of three-axis displacement sensors, receiving technological signals of pressure and temperature in a steam generator;
- continuously remotely monitoring pipeline displacement by three mutually perpendicular axes and maintaining a database;
- providing an operator with pipeline displacement information as videograms;
- transferring information on displacements and violations of permissible displacement limits to adjacent systems;
- providing power unit personnel with information on faults and failures, generating alarm on impermissible pipeline displacements.






